Overview
CRDS (Calibration References Data System) is a Python library, set of command line programs, and family of web servers used to assign and manage the best reference files that are used to calibrate HST and JWST data.
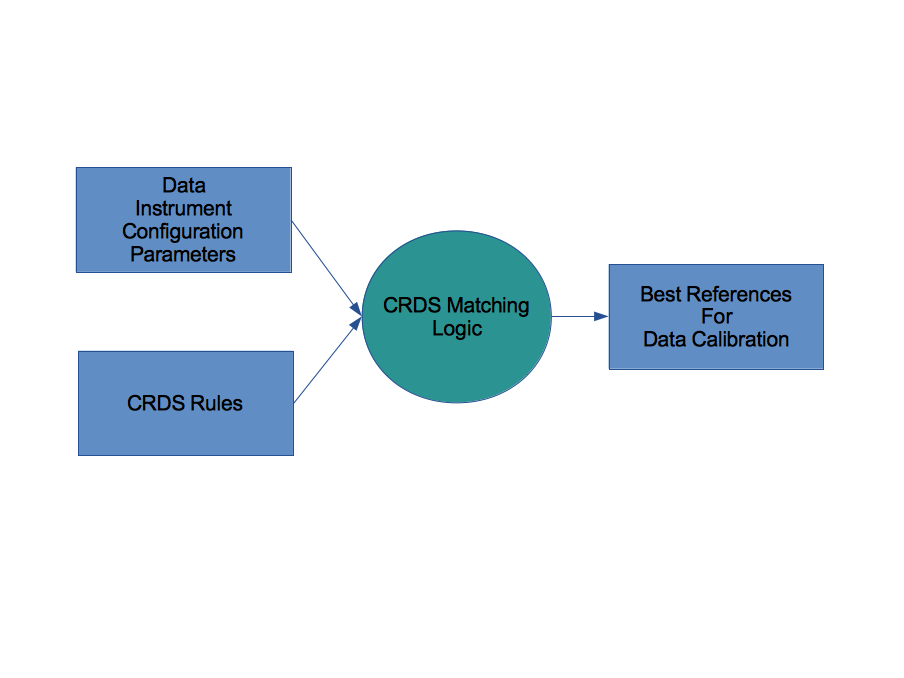
CRDS Matching
The primary function of CRDS is to assign best reference files to datasets so that they can be calibrated based upon CRDS rules.
CRDS revolves around a hierarchy of plain text rules files that define reference file assignments:
Properties of CRDS
1. CRDS rules are versioned. Given the same instrument configuration, the results produced by CRDS at any given point in time are reproducible.
Since CRDS rules are versioned, bad rule updates can effectively be undone.
CRDS Rules
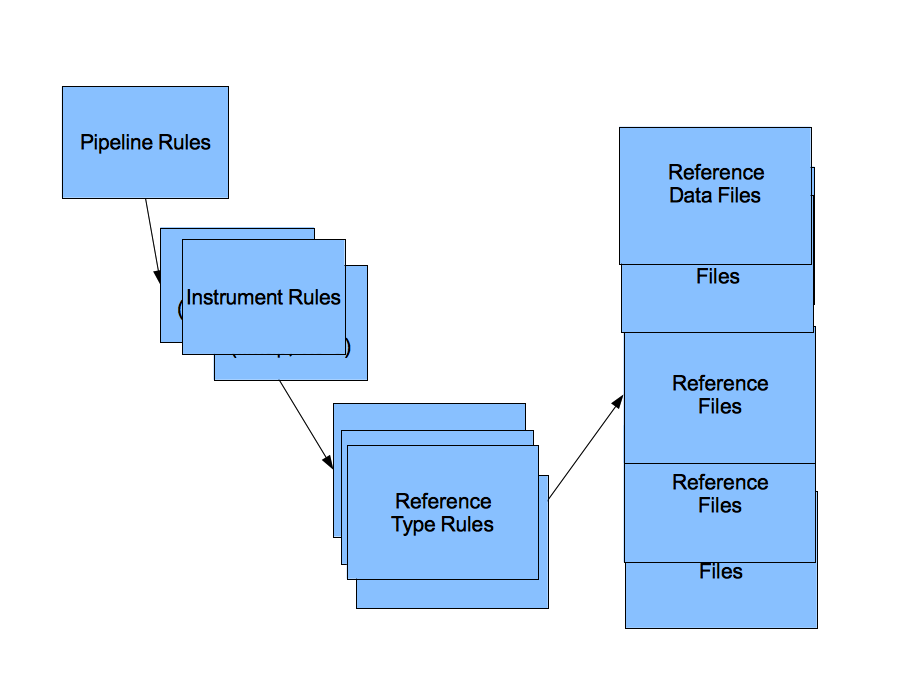
The CRDS rules hierarchy has 4 tiers corresponding to the overall pipeline configuration, the current rules for each instrument, the rules for each type of each instrument, and finally individual reference files assigned by instrument configuration and date:
Kinds of CRDS Files
References are assigned by descending the CRDS rules hierarchy.
Class of File |
Extension |
Quantity |
Example Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Pipeline Context |
.pmap |
1 |
hst_0001.pmap |
Governs all instruments for one project |
Instrument Context |
.imap |
5-6 |
hst_acs_0047.imap |
Governs all types for one instrument |
Reference Type Mapping |
.rmap |
100-130 |
hst_acs_darkfile_0107.rmap |
Governs one type for one instrument |
References |
.fits, .asdf, etc. |
1000’s |
lcb12060j_drk.fits |
Individual reference files |
Each calibration requires many types of references that vary by instrument and mode. Each pipeline context defines a specific CRDS configuration (rules version) for the archive pipeline at one point in time.
References are defined by descending the hierarchy based on exposure configuration parameters such as EXP_TYPE, FILTER, etc.
CRDS rules files have a number of properties and implications:
1. The name of every rules file has a serial number / version
2. Rules group reference files into succinct mode-based categories.
3. References within a category are generally differentiated by USEAFTER date.
4. No database account or SQL queries are required to review or plain text rules files.
5. While the websites provide tabular displays, the rules files are directly readable.
6. CRDS caching mechanisms avert the need for a constant connection to the CRDS servers.
7. CRDS rule updates can effectively be undone by reverting to a prior version.
CRDS Tools
In addition to assigning best reference files based on a hierarchy of rules, CRDS provides tools to check, difference, and generally manage a cache of rules and reference files. Individual programs are managed under the “crds” master script:
- crds bestrefs
Best references utility for HST FITS files and context-to-context affected datasets computations.
- crds sync
Downloads and manages a cache of CRDS rules, references, and state information.
- crds certify
Checks constraints and format for CRDS rules and references.
- crds diff, crds rowdiff
Difference utility for rules and references, also FITS table differences.
- crds list
Lists cache files and configuration, prints rules files, dumps database dataset parameter dictionaries.
- crds matches
Prints out parameter matches for particular references.
- crds uses
Lists files which refer to (are dependent on) some CRDS rules or reference file.
Each sub-command can also be invoked as follows:
$ crds sync --help
to print help information, where –help must be specified as the first parameter to the sub-command.
CRDS Web Sites
The CRDS web sites manage CRDS rules and reference files and metadata:
Project
Use Case
URL
HST
Operations
HST
Pipeline Test
JWST
Operations
JWST
Pipeline Test
ROMAN
Operations
ROMAN
Pipeline Test
A number of additional servers exist to support development and I&T for JWST and Roman.
The CRDS web servers provide these functions:
Cataloging and display of information about CRDS files.
Tabular display of the latest rules in the archive pipeline.
Maintains and displays history of contexts used by the archive pipelines.
Supports the CRDS client library.
File submissions and archiving.
File and configuration distribution.
CRDS file differencing.
Team activity and delivery tracking.
Automatic determination of datasets to reprocess based on new references and/or rules.
Server Functions
Reference Ingest
Another major function of CRDS is to support the addition, deletion, and replacement of reference files and rules. Reference and rules ingest includes these additional functions:
Reference and rules file certification and checking.
Automatic rules updates based on submitted reference files.
File delivery to an archive ingest interface.
File metadata cataloging.
Context Management
The current version of CRDS rules that is active in the archive pipeline is tracked on the CRDS server. Pipeline operator’s choose when to activate fully delivered CRDS files in the pipeline. CRDS maintains:
A dated history of the current and past pipeline contexts, including a change rationale.
An echo of the last default context sync’ed to the pipeline.
An ability to inspect the differences between any two contexts.
The ability for end user’s to select a non-default context.
File Distribution (cache sync)
One of the new features of CRDS is provision for the download and management of rules and reference files in two ways:
1. The crds sync tool supports downloading all the references in a selection of CRDS contexts, e.g. all contexts, the last 5 contexts, etc. The complete caches consume terabytes of space.
2. The crds bestrefs tool and/or JWST and Roman CAL code direct integration can dynamically download references applicable to a group of particular datasets. Dynamic downloads and private caches can improve upon VPN for remote users since cached CRDS references are only downloaded once.
In both cases the quanity of files downloaded has no arbitrary bound; if files are listed in the CRDS rules or assigned by the bestrefs program or JWST/Roman CAL code, CRDS can download all of them.
Reprocessing Support
One of the new features of CRDS is the ability to recommend the set of datasets that are candidates for reprocessing based on newly delivered references.
CRDS computes affected datasets by comparing the references assigned by old and new contexts based on archived dataset parameters for applicable datasets.
The CRDS reprocessing system is fully autonomous and triggered by the selection of a new default contextr by a pipeline operator. After running to completion, the reprocessing system stores logs and recommended datasets personally and makes them available via e-mail and a web interface and client program.
Web Services
The CRDS servers provide a variety of web services via JSONRPC interfaces, including a JSON rendering of the current JWST or Roman CAL s/w component versions and a best references web service for the archive. Additional web services support file distribution and reprocessing functions.
Web Displays
The CRDS web servers provide an accurate rendition of the current and past rules in a tabular format as well as simple text displays of the rules files.
CRDS supports differencing two contexts to review changes.
CRDS tracks team activity and file deliveries to support reviewing ongoing work and changes.